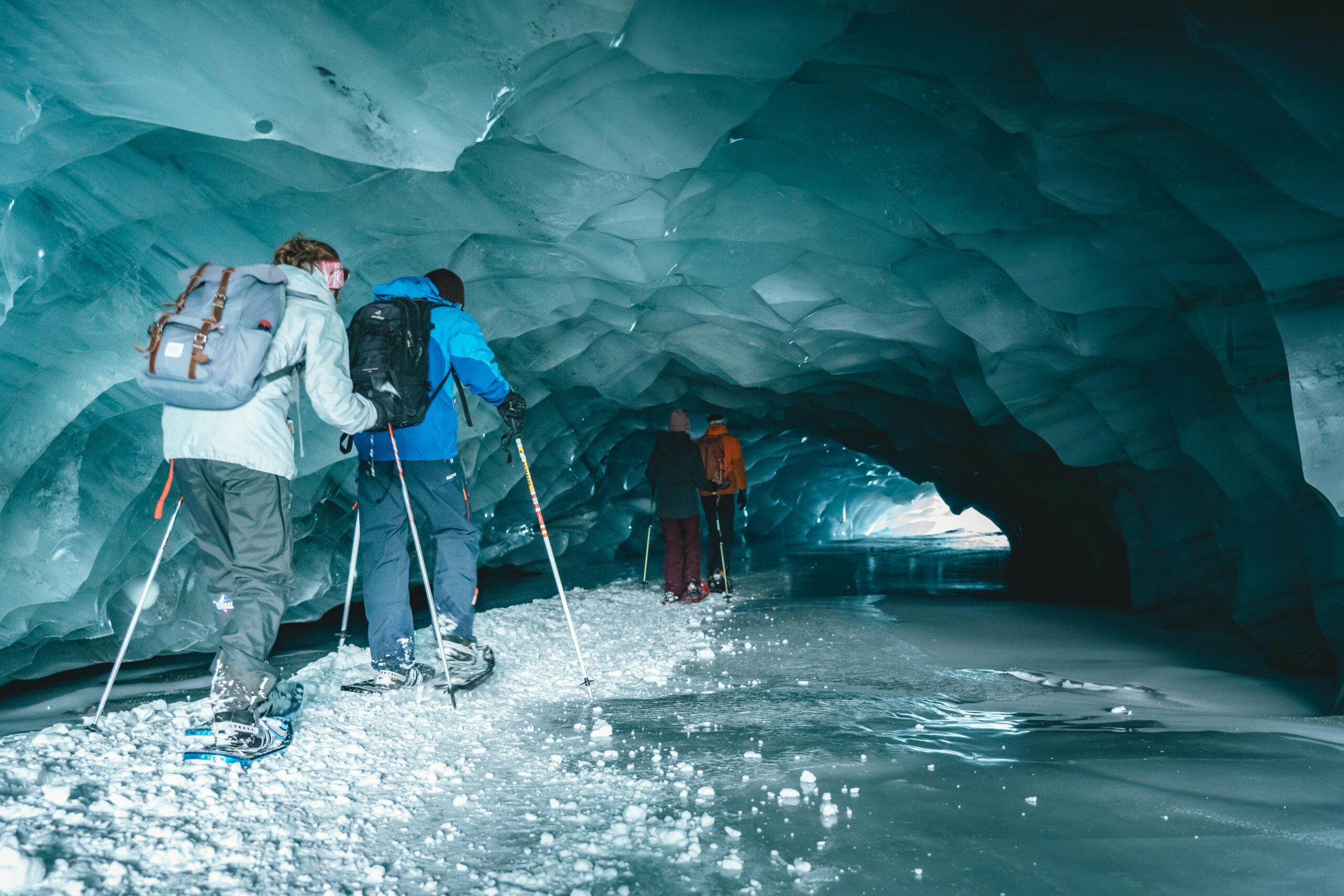
Chinese astronauts have just wrapped up a grueling underground survival exercise, braving dark, sealed caves for nearly a month to hone skills critical for landing on the moon. The training, involving 28 astronauts divided into teams, is a key step in preparing for China’s planned crewed lunar missions set for before 2030.
In the mountainous terrain of Chongqing, teams spent sessions of six days and five nights in cold, humid caves, deliberately isolated from easy support. The program, organized by the China Astronaut Research and Training Center, was designed to mirror the psychological and physical demands of deep space. “The cave was sealed, in complex terrain, dark and wet,” Zhu Yangzhu, China’s first spaceflight engineer, told Xinhua. “It re-created the solitude and unknowns of deep space exploration, challenging our physical and mental limits.”
The training focused on core expedition skills like environmental monitoring, 3D cave mapping, and simulated communications with a mission control-like ground team. Instructors, including Ye Guangfu, a veteran of the Tiangong space station and a 2016 ESA CAVES participant, threw in unexpected medical emergencies to test crisis response. Crucially, the support team intervened as little as possible. “This approach pushed astronauts to rely on their own judgment, unlocking both individual initiative and their full problem-solving potential,” Ye explained, according to the Xinhua report.
READ ALSO: https://modernmechanics24.com/post/indian-navy-awards-torpedo-contract-wass/
This marks China’s first implementation of training similar to the European Space Agency’s (ESA) renowned CAVES program. Beyond the underground ordeal, each session included two days of jungle survival training. The data collected on team dynamics and stress responses is invaluable. “The data will provide crucial support for establishing psychological support systems for astronauts undertaking long-duration space station missions and crewed lunar landing missions in the future,” said instructor Jiang Yuan to China Central Television (CCTV).
The training’s completion was announced on a symbolic date: the 28th anniversary of the founding of the Chinese Astronaut Corps. This intensive preparation is part of a clear, accelerating roadmap. China aims to land two astronauts on the moon for a short stay before 2030. The mission architecture involves two Long March 10 rockets launching separately—one carrying the Mengzhou crew spacecraft and the other the Lanyue lander—which will dock in lunar orbit before descending.
WATCH ALSO: https://modernmechanics24.com/post/us-supersonic-jet-cuts-flight-time-silences-sonic-boom/
The hardware is rapidly taking shape. In 2025, China conducted a series of critical tests, including a static fire for the Long March 10 rocket and a pad abort test for Mengzhou. A full, uncrewed test flight of the Long March 10A rocket is scheduled for 2026. The broader ambition is the construction of the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) in the 2030s.
This push places China squarely in a new era of lunar exploration, potentially setting the stage for a historic parallel achievement. NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the lunar surface with Artemis 3, currently targeting 2028. As both superpowers prepare for lunar landings, China’s astronauts are now training in some of Earth’s most extreme environments to ensure they are ready for the ultimate extreme environment: the surface of the moon.