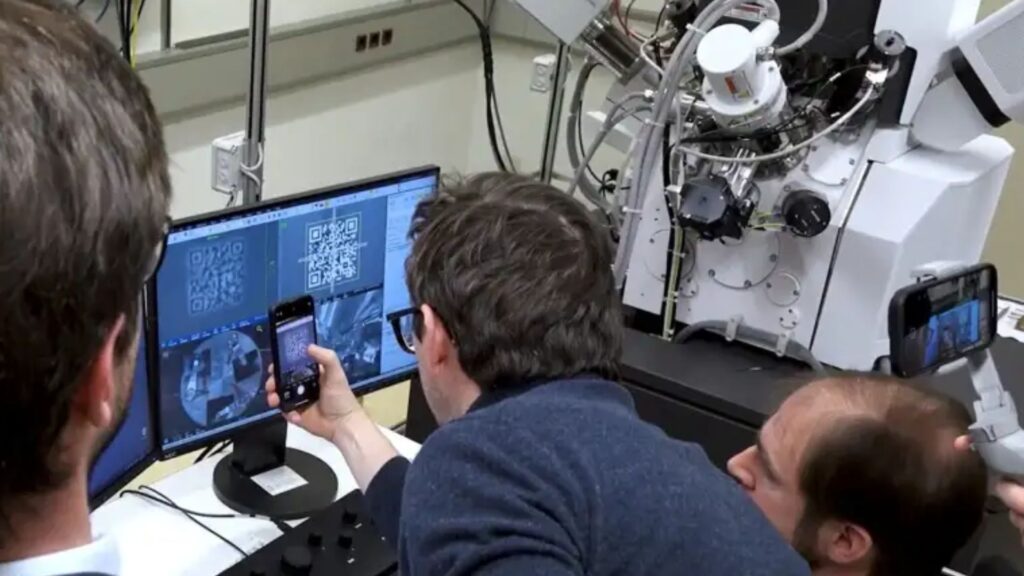
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory have developed key battery technologies that are helping American companies manufacture advanced energy storage systems and compete globally.
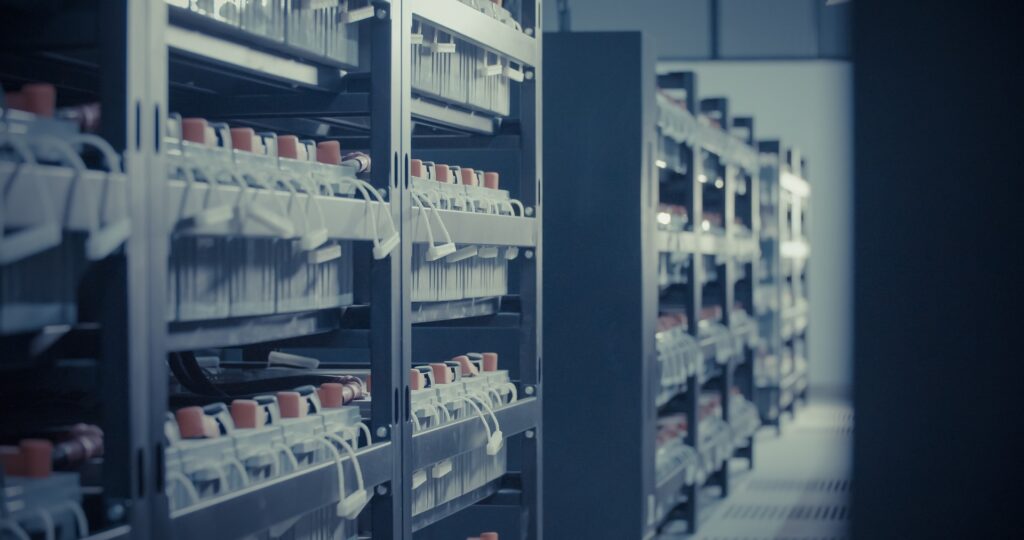
The lab’s research into materials like nickel-manganese-cobalt electrodes has laid the groundwork for today’s lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles and grid storage, while strengthening domestic supply chains.
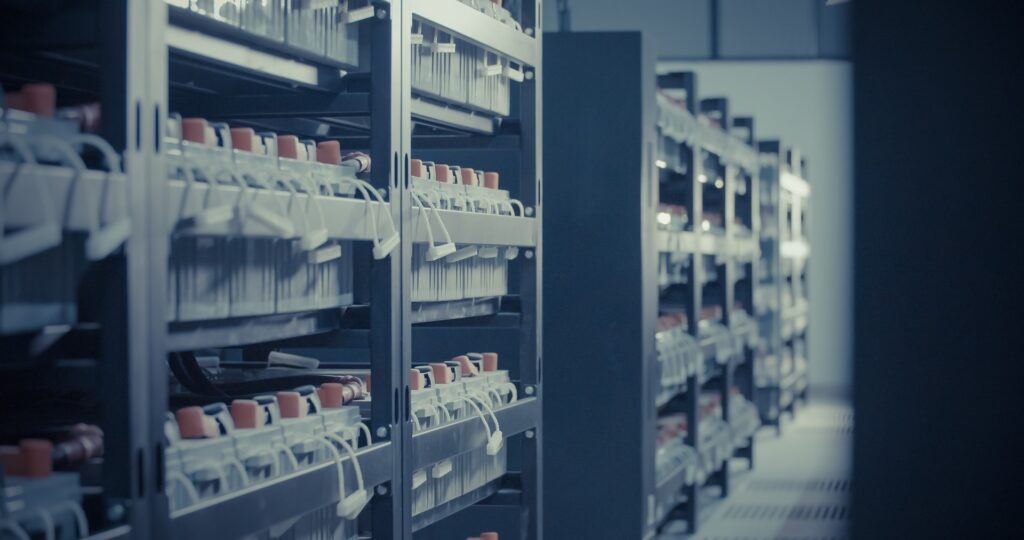
Argonne National Laboratory has a long history of battery research that directly benefits U.S. industry. The lab holds more than 250 active energy storage patents and licenses its breakthroughs to companies for mass production. These collaborations have created American jobs and led to new manufacturing plants. The work covers multiple battery technologies including lithium-ion, solid-state, flow batteries, and sodium-ion alternatives.
Argonne National Laboratory, part of the U.S. Department of Energy, conducts this research through its Collaborative Center for Energy Storage Science. Venkat Srinivasan, director of the center, leads a multidisciplinary team that works with dozens of companies. Industry partners include General Motors and LG Chem, which license Argonne technologies to produce patented battery materials at scale.
READ ALSO: https://modernmechanics24.com/post/machine-eye-beats-human-vision-speed/
The U.S. has relied heavily on foreign supply chains for critical battery materials like lithium and cobalt. This creates vulnerabilities for industries ranging from electric vehicles to defense. Argonne’s collaborations help cultivate domestic sources of these materials and develop alternative battery chemistries that use abundant U.S. resources, reducing reliance on imports.
Companies can work with Argonne in several ways. Battery entrepreneurs use the lab’s world-class facilities and work with researchers to develop promising concepts. Dozens of companies engage in joint research projects, often privately funded. Argonne transfers its intellectual property through licensing agreements, allowing companies to mass-produce advanced battery materials. For example, the lab is working with a domestic lithium producer to develop cost-effective methods to refine lithium from brines in U.S. underground reservoirs, yielding battery-grade lithium hydroxide.
Argonne’s innovations support multiple sectors. For electric vehicles and grid storage, the lab’s foundational research on nickel-manganese-cobalt electrodes enabled today’s high-energy lithium-ion batteries. For grid resilience, the lab works with industry to improve lead-acid batteries that power telecommunications and critical infrastructure, and explores ways batteries can support data centers during peak demand. For defense applications, Argonne develops safer, longer-lasting battery chemistries for unmanned aerial vehicles, military vehicles, and radios that must perform in extreme environments like low temperatures.
WATCH ALSO: https://modernmechanics24.com/post/ubtech-world-first-robot-shipment/
While Argonne’s research has enabled significant advances, challenges remain. Sodium-ion batteries, which offer an alternative to lithium using abundant U.S. materials, are still emerging and not yet as energy-dense as lithium-ion. Refining lithium from domestic brines requires further development to become cost-competitive with foreign sources. The lab continues working with industry to overcome these hurdles.
These battery breakthroughs support American manufacturing, national security, and economic competitiveness. Venkat Srinivasan said Argonne’s capabilities span the entire energy storage ecosystem, from material discovery to device testing. By helping U.S. companies become commercially successful global leaders, the lab reduces reliance on foreign supply chains, creates domestic jobs, and ensures mission readiness for defense applications. The work also supports grid resilience by enabling batteries to power critical infrastructure and data centers reliably.