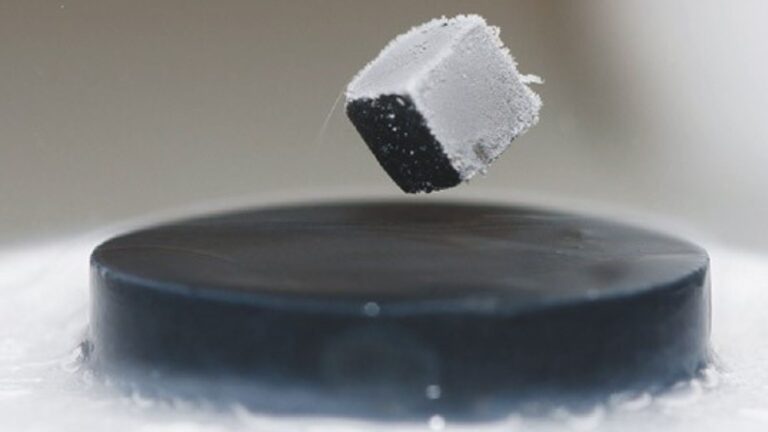
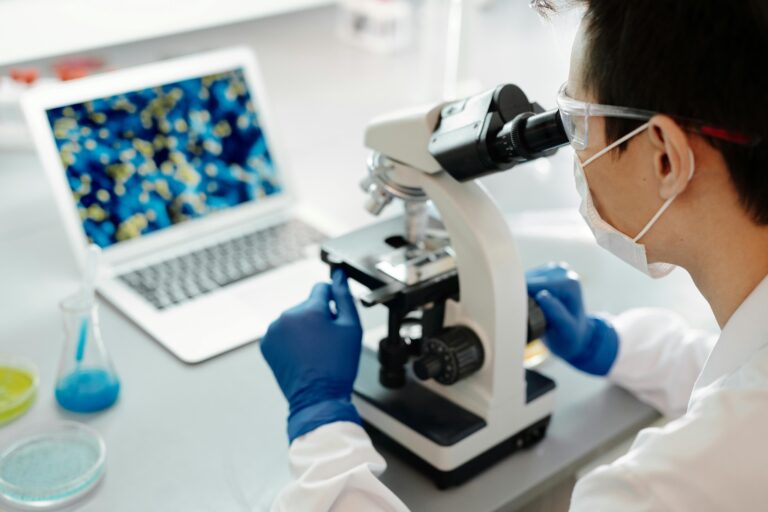
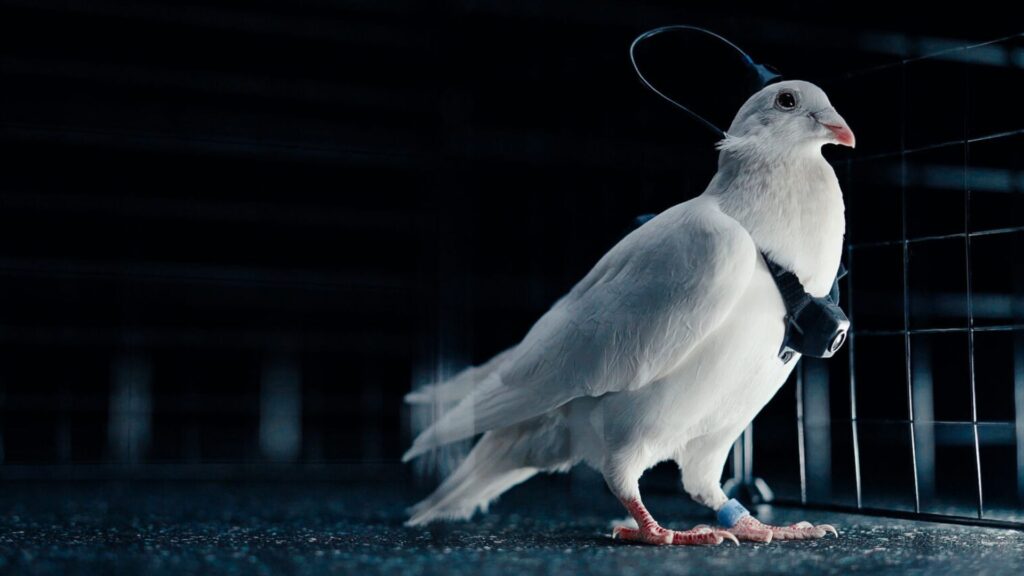
Begonia pingxiangensis (image by XI Houcheng)
Begonia is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Begoniaceae, comprising more than 2000 species. In China, 288 species including subspecies, varieties and natural hybrid species have been recognized.
In a study published in Taiwania, researchers from Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported an unknown Begonia species with relatively small leaves collected on a limestone mountain during a field survey of Pingxiang City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China in November 2020, and brought it into cultivation in the garden.
After consultation of herbarium specimens and review of relevant literature, researchers confirmed that this species is new to science. They named it Begonia pingxiangensis to refer to the type locality in Pingxiang, Guangxi, China.
Begonia pingxiangensis is a perennial herb to 20 cm tall. It resembles Begonia daxinensis in the leaf and flower, but can be distinguished by its leaf blade shape (ovate to broadly ovate vs obliquely ovate to suborbicular), size (4-8 × 3-7 cm vs 10-24 × 10-17 cm), flower color (white vs white or pinkish), smaller staminate flower and pistillate flower (outer two tepals 7-8 × 8-10 mm; inner one 3-4 × 2 mm vs outer two tepals 10-15 × 10-12 mm; inner one 5-7.5 × 2-5 mm) sizes.
The new species is endemic to Guangxi, and is currently only known from Puzhai Community, Youyi Town, Pingxiang City. It grows on rock surface under the forest of karst mountains at an elevation of 320 meters.
Begonia pingxiangensis is only known from the type locality with five small subpopulations of less than 60 mature individuals in nearly 2 km2. Researchers thus assessed its conservation status as Endangered (EN) based on the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria.