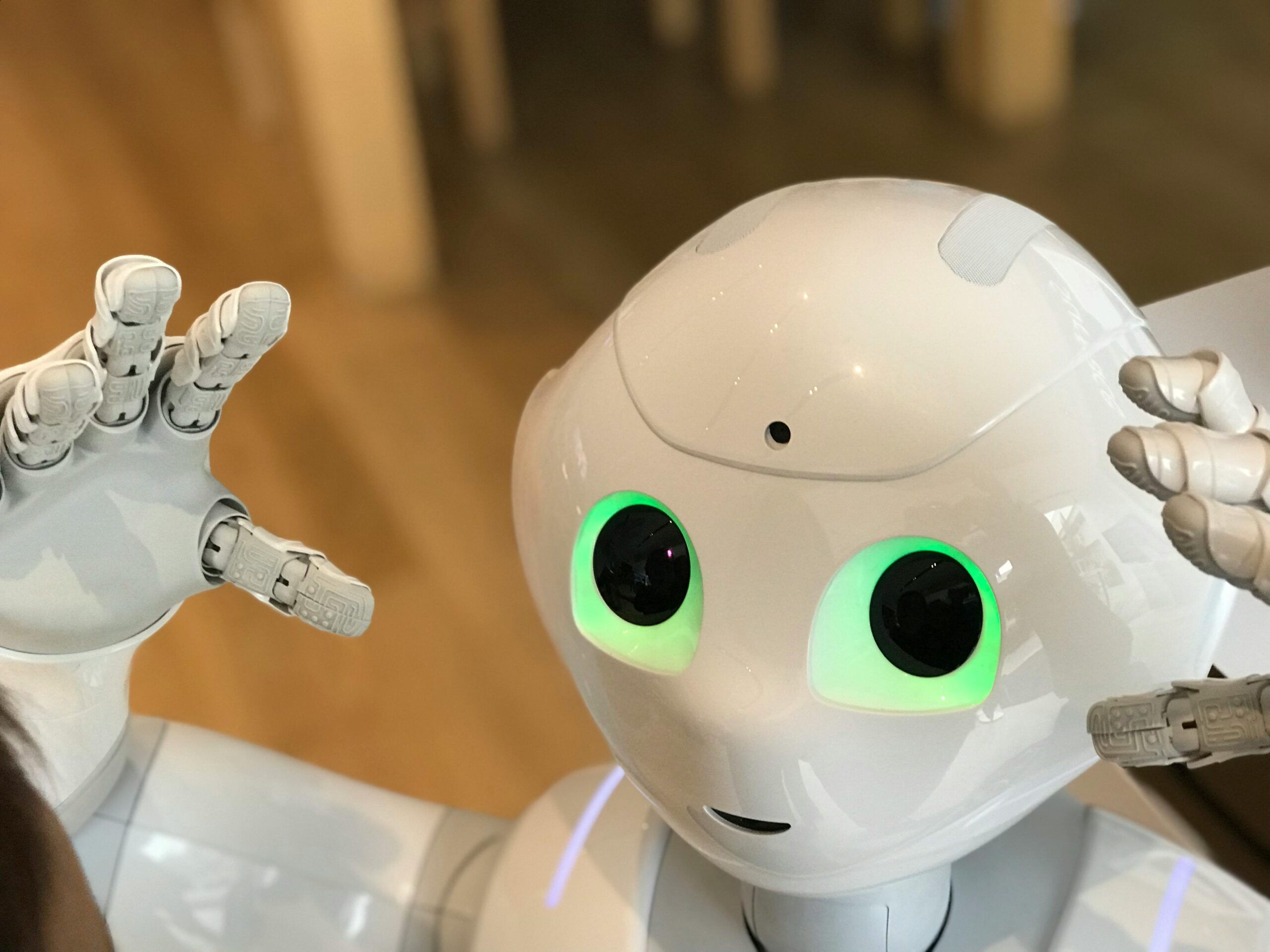
Alibaba’s DAMO Academy has unveiled RynnBrain, a family of open-source embodied AI models that set 16 new benchmark records and outperform Google’s Gemini Robotics ER 1.5 and NVIDIA’s Cosmos Reason 2. Led by Director Zhao Deli of the Embodied AI Lab, the breakthrough gives robots what they have always lacked: spatiotemporal memory and physical-space reasoning.
For all the talk of intelligent machines, robots have suffered from a peculiar form of amnesia. They see what is in front of them, but they forget what they saw a moment ago. Walk into a kitchen, ask a robot to fetch an apple, then interrupt it with a second request—and the first task vanishes from its mind as if it never existed. Alibaba’s DAMO Academy, based in Hangzhou, has now given robots something close to recollection.
The product solves a problem that has quietly plagued embodied AI for years. Traditional systems operate frame by frame, treating each moment as isolated. They have no episodic memory. They cannot track an object across time, nor recall where something was positioned before they looked away. RynnBrain changes that through what its creators call spatiotemporal memory—the ability to locate objects, regions, and motion paths across a robot’s complete history of experience .
READ ALSO: https://modernmechanics24.com/post/sunlight-liquid-metal-clean-hydrogen/
What it actually does for users is deceptively simple. A robot running RynnBrain can be told to place a cup on a table, interrupted to open a drawer, and then resume the first task without needing to re-scan the environment. It remembers the cup’s location, the table’s position, and the stage of completion. This is not trivial. According to Director Zhao Deli, who leads the Embodied AI Lab at DAMO Academy, “RynnBrain achieves, for the first time, a depth of understanding and reliable planning in the physical world. It marks a key step toward general embodied intelligence under a hierarchical brain‑cerebellum architecture” .
The underlying mechanism is a hybrid reasoning strategy. Unlike conventional models that reason purely through text, RynnBrain alternates between textual logic and spatial grounding. Every inference is anchored to physical coordinates, which dramatically reduces the hallucination problem that plagues AI when it tries to describe the real world . The model was trained on Qwen3-VL, Alibaba’s vision-language system, and optimized using a custom architecture called RynnScale, which doubled training speed on the same compute budget .
There is, of course, a limitation. RynnBrain is a brain, not a body. It performs cognition, localization, and planning—but it does not control motors directly. The model outputs spatial trajectories, grasp poses, and action sequences, which must then be executed by lower-level control systems . The team acknowledges that bridging the gap between high-level planning and real-world actuation remains an open engineering challenge, particularly in unstructured environments where friction, lighting, or material properties defy simulation.
WATCH ALSO: https://modernmechanics24.com/post/hmnd-01-alpha-simulation-humanoid-robot/
Still, the summary value is unmistakable. Alibaba has not merely released a research paper; it has open-sourced seven full models, including the industry’s first 30-billion-parameter mixture-of-experts embodied model, which activates only 3 billion parameters during inference yet outperforms conventional 72-billion-parameter systems . That efficiency translates directly to faster, smoother robot motion. The company also released RynnBrain-Bench, a new evaluation framework for fine-grained spatiotemporal tasks, filling what the team calls a “gap in the industry” .
The innovator behind the architecture is Zhao Deli, Director of the DAMO Academy Embodied AI Lab. The engineering was executed by a multidisciplinary team that has spent years building foundational models for physical intelligence, including the open-source WorldVLA and the RynnEC world understanding model . Their decision to release everything—weights, training code, inference pipelines—signals a deliberate strategy. According to Bloomberg, the open-source approach contrasts sharply with the guarded posture of some U.S. competitors and could accelerate research worldwide .
The timing is not accidental. China has designated physical AI and humanoid robotics as national priorities in its competition with the United States. Alibaba is now one of several Chinese giants placing large bets on embodied systems. As reported by Saba and CNBC Arabia, the company is leveraging the momentum of its Qwen model family, already among the most advanced large language models to emerge from China.
READ ALSO: https://modernmechanics24.com/post/china-first-humanoid-robot-for-autism/
Whether RynnBrain becomes the Android of robotics—an open foundation upon which an entire industry builds—remains to be seen. But for the first time, a Chinese tech firm has released an embodied AI model that matches or exceeds Western counterparts on nearly every published benchmark. And it has given it away for free.